This piece was first posted on the University of Washington Department of Global Health’s (DGH) website.

A new five-year research project will study two-way texting as a means of communication between healthcare providers and male circumcision (MC) patients in South Africa. It will build on previous research conducted in Zimbabwe.
Caryl Feldacker is the Principal Investigator (PI) on this RO1, which will support research through 2025. The multi-stage implementation science study is based out of the International Training and Education Center for Health (I-TECH), and will be implemented with Dr. Geoffrey Setswe, PI for South Africa partner, Aurum Institute, and with technology partner, Medic Mobile.
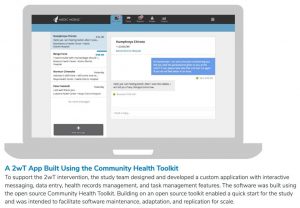
“Previous research shows that healthcare workers waste a lot of time and money reviewing MC clients without complications,” Feldacker said. “So, in partnership with Medic Mobile, we developed a two-way texting (2wT) system to identify and refer men with potential medical issues to in-person care while allowing the vast majority to opt-out of routine post-operative visits.”
Programs providing voluntary medical male circumcision (MC) in sub-Saharan Africa are struggling to meet the annual goal of 5 million MCs. However, chronic human and financial resource shortages threaten achievement of MC targets, reducing impact of this effective HIV prevention intervention. Although MC is safe with an adverse event (AE) rate of less than 2% , global MC guidelines require one or more in-person, post-operative visits within 14 days of MC for timely AE identification. With low AE rates, overstretched clinic staff likely waste invaluable resources conducting unnecessary routine reviews for MC clients without complications while men healing well needlessly pay for transport, miss work, and wait for reviews, discouraging MC uptake.
With this background, Dr. Feldacker’s prior randomized controlled trial (RCT) in Zimbabwe tested whether 2wT between patients and providers during the critical 13-day post-operative period (instead of routine in-person reviews) could ensure patient safety while reducing provider workload. 2wT safely reduced client visits by 85%, increased AE identification, and cut follow-up costs, suggesting that 2wT could make a dramatic difference in MC programs operating at scale. Plus, providers and patients found the 2wT follow-up approach highly usable and acceptable. “These daily text exchanges really empowered men to be partners in their healing process, creating a win-win for providers and patients.”
Read the entire story on the DGH website.