Voluntary medical male circumcision (VMMC) decreases the risk of female-to-male HIV transmission by about 60%.[1] I-TECH Network partner the Zimbabwe Technical Assistance, Training, and Education Center for Health (Zim-TTECH) supports innovative VMMC engagement solutions that are tailored to the populations they serve.
Caravans Allow for Mobile Services and Door-to-Door Outreach

Makumbe Hospital in Goromonzi District, Zimbabwe, serves a population of more than 100,000 people, including the rapidly expanding population of surrounding townships. Zim-TTECH-led consortium ZAZIC has run the Makumbe Hospital site since October 2018 and supports the VMMC team there.
This population within the hospital’s catchment area primarily comprises informal traders selling necessities such as groceries, garden produce, or second-hand clothes, while others run at-home small businesses that manufacture furniture, iron and steel products, and other wares.
“It’s difficult for economically active young men to leave their businesses and attend to VMMC at a venue away from their premises or market,” said Lewis Masimba, VMMC Program Manager at Zim-TTECH.
In light of this challenge, the team implemented a mobile caravan, which could increase the number of men receiving circumcisions by taking services out of the medical facility and bringing them closer to the concentrated settlements of Domboshava Showground, Mungate, and Mverechena townships and nearby farm compounds.
The caravan has been in use in the district since January 2023, and it has vastly shortening the period between client engagement and service delivery. In most cases, two mobilizers at a time will engage with potential clients within the townships, while another three will conduct intensive door-to-door visits in residential areas.
Mobilization efforts include one-on-one and small group discussions at market stalls, small businesses, and drinking spots, where mobilizers will answer questions and distribute information about VMMC. Sometimes the caravan is supported by a roadshow van and dancers who disseminate VMMC information through edutainment.
“The caravans have so many advantages,” said Mr. Masimba. “Men are able to access the VMMC services near their workplaces, minimizing disruptions to their daily routines. The caravan has also brought convenience and privacy to those who did not feel comfortable being ferried in program vehicles to and from the hospital.”
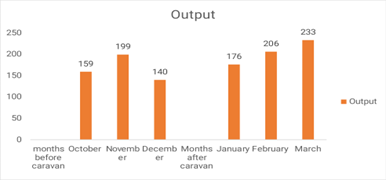
Since the site started utilizing the caravan, the number of men who have received VMMC each month has increased from 159 to 233 (Fig. 1).
On the heels of this success, the ZAZIC teams will continue exploring other combination approaches involving engagement activities such as pool/snooker, soccer, and music roadshows to reach hard-to-convince men in their localities.
Peer-to-Peer Learning Takes Center Stage in Performing Arts Program for Adolescents

The performing arts have been used since time immemorial as motivators to rally communities toward common goals, to relieve stress, and as an effective teaching tool across diverse cultures and religious settings. They are a particularly effective method for engaging adolescents both in and out of schools. As teens seek independence from their parents, the influence of peers becomes increasingly important, and performing arts are a fantastic way to employ peer-to-peer learning strategies.
Harnessing these strategies, ZAZIC uses drama in several districts to complement efforts already made by VMMC teams and teachers who have previously used sporting events and lectures to communicate with students.
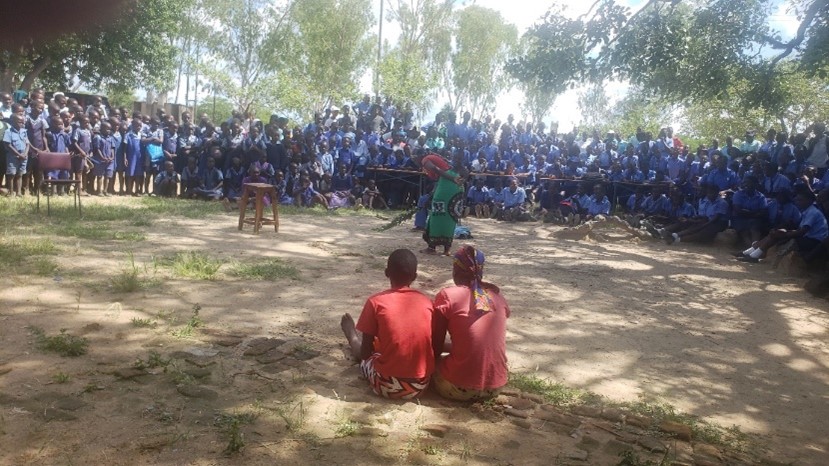
In a particularly successful case, Hurungwe District chose to use a drama competition to communicate VMMC and other health messages to adolescents. The goals of the competition included effective peer-to-peer learning, outreach to a large audience, and the demystification of VMMC.
Roadshows to promote the competition were held at major townships to create awareness of the event and invite members of the public to attend. Eight secondary schools enrolled in the competition, and teams of adolescents led the process of writing and directing short, 30-minute performances incorporating messages in a provided guide.
The guide emphasized use of appropriate language, the need to double-check facts; and encouragement of uptake of VMMC and related services, such as HIV testing and counseling and cervical cancer screening.
More than 1,000 people attended, including students, parents, and staff from all competing schools.
“Matawu Secondary School ultimately won the drama competition, but all of the schools did a wonderful job explaining VMMC and its benefits,” said Mr. Masimba. “Messaging also emphasized abstinence for adolescents, the importance of the HPV vaccine for girls, and details about the VMMC procedure. The level of accuracy of information was extremely high.”
Importantly, two of the performances highlighted communities that reject medical interventions and stressed the need for participation by all.
A total of 182 VMMCs were attained by adolescents aged 15 to 19 years old immediately after the competition. Those who were not ready were booked for the procedure and will be followed up with by school health masters and community mobilizers.
[1] https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/72/wr/mm7210a2.htm